Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is transforming the way industries manage transactions and data. Originally built for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its decentralized and tamper-proof architecture is now empowering sectors ranging from supply chain to voting systems.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
What Is Blockchain?
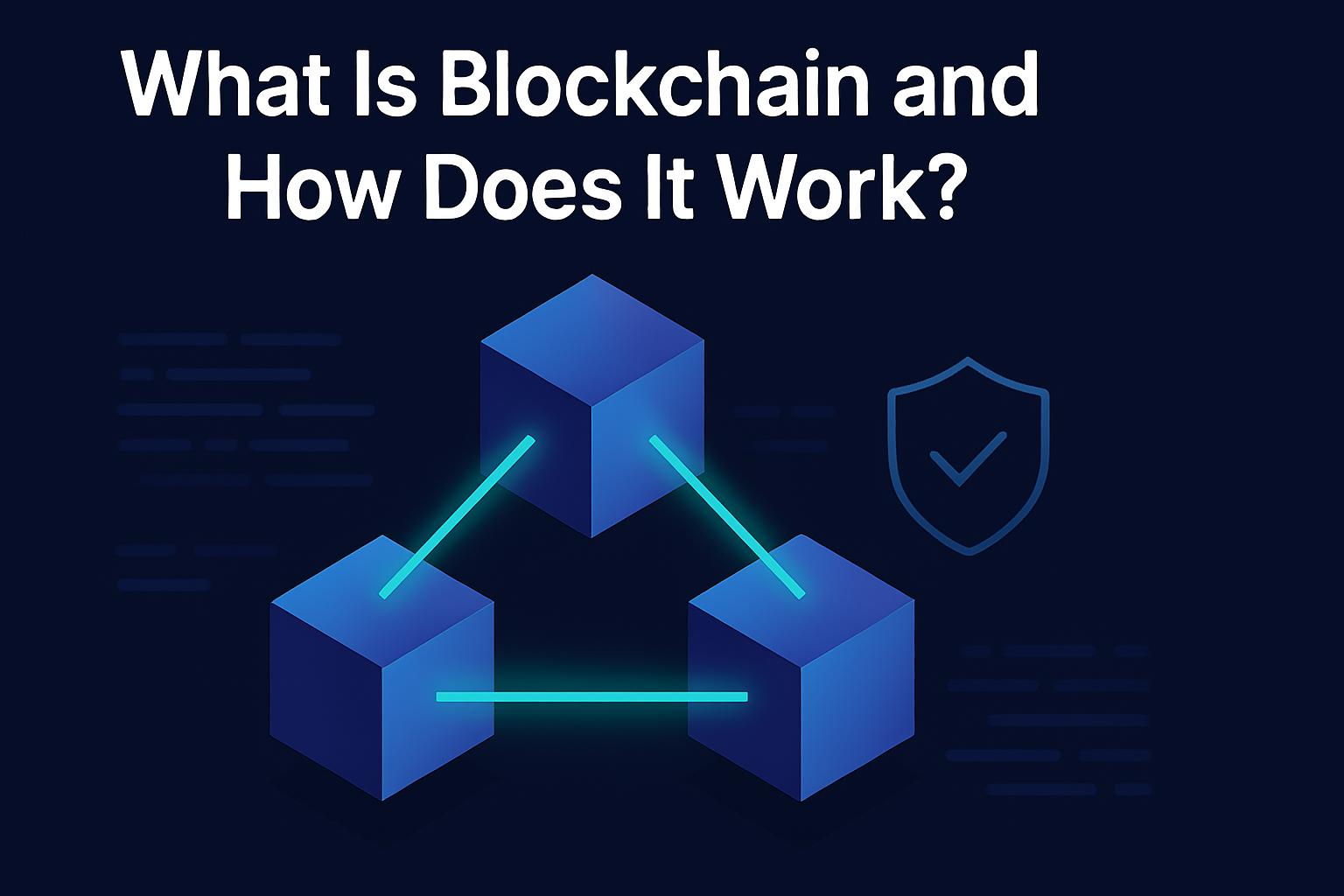
Blockchain is a distributed, digital ledger system where information is grouped into blocks and securely linked together. Unlike traditional databases, blockchains are not controlled by a central authority. Every transaction is transparent, cryptographically verified, and immutable once added to the chain.
A Brief History of Blockchain
The foundation of blockchain was laid in the 1990s when cryptographers Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta created a method to timestamp digital documents. Their work inspired the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, the first application of blockchain for decentralized currency. Since then, adoption has exploded globally.
Core Features of Blockchain
1. Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a network of nodes, not a single server, enhancing resilience and reducing the risk of hacks.
2. Transparency
Public blockchains allow anyone to view transactions via blockchain explorers, increasing trust.
3. Immutability
Once recorded, data cannot be altered without consensus from the network.
4. Cryptographic Security
Advanced encryption ensures the accuracy and privacy of every transaction.
5. Speed and Efficiency
Transactions are processed faster and cheaper by eliminating intermediaries.
How Blockchain Works
Step 1: Transaction Broadcast
When a transaction is made, it is broadcast to the network for validation.
Step 2: Block Creation
Validated transactions are bundled into a block with a timestamp, data, and cryptographic hash.
Step 3: Consensus Mechanism
Nodes agree on the validity of the block using Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
Step 4: Chain Addition
The new block is appended to the blockchain, referencing the previous block’s hash.
Step 5: Public Record
Every transaction is viewable on public ledgers for maximum transparency.
Blockchain and Cryptography
H3: Cryptographic Hashing
Hashing algorithms like SHA-256 convert data into a fixed-length string. Any minor change in input yields a dramatically different hash, ensuring data integrity.
H3: Public-Private Key Pair
Users have a public key (visible) and a private key (secret). Transactions are signed using the private key and verified with the public one—guaranteeing secure identity verification.
Consensus Mechanisms Explained
Proof of Work (PoW)
Used by Bitcoin. Miners solve complex problems to validate transactions and are rewarded in crypto.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Used by Ethereum 2.0. Validators are chosen based on their staked coins.
Other Models
-
DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) – Elected validators represent the network.
-
PoA (Proof of Authority) – Reputation-based validation model.
Types of Blockchain Networks
H3: Public Blockchain
Open to all, fully decentralized, and transparent. (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
Private Blockchain
Access is controlled by a central entity. Often used in businesses for internal processes.
Consortium Blockchain
Governed by a group of organizations. Blends elements of both public and private chains.
Real-World Uses of Blockchain
1. Cryptocurrencies
Used as a decentralized record of digital currency transactions like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
2. Smart Contracts
Self-executing agreements without the need for intermediaries.
3. Tokenization of Assets
Convert real-world assets like real estate or artwork into digital tokens.
4. Digital Identity
Create tamper-proof identities that can be securely verified online.
5. Secure Voting
Enable tamper-proof, transparent voting systems.
6. Supply Chain Tracking
Track goods in real time across every step of the supply chain.
Closing Thoughts
Blockchain is much more than a buzzword—it’s a powerful shift in how we record, validate, and trust digital information. As it matures, we’ll continue to see it disrupt more industries and redefine trust in the digital age.